Rejuvenate your aging road surfaces with a refreshing ACP Applied Products fog seal.
As roads bake beneath the sun, heat and oxygen can contribute to oxidation: the hardening of the bitumen binder. This results in a brittle road surface that can chip and crack easily. A fog seal will help regenerate the brittle bind, lock in stones and improve stone retention when used on chip and gravel seals.
A fog seal is an emulsion sprayed over an existing surface. Applying a fog seal can mitigate brittle binder and cracking, extending road life and preserving existing seals. Other benefits of ACP Applied’s fog sealing service include:
- High speed
- Minimal cost
- New, black look
- Fills microcracks
- Restores waterproofing
Thanks to their versatility, fog seals are an excellent choice for renewing roads. With the options of using a trackless emulsion that won’t pull off onto tires, quick setting emulsions to get traffic going again sooner, or a sand seal that fills in larger voids and restores texture, ACP Applied can provide the sealing and rejuvenating service you need to maximize the lifespan of your roadways.
Fog Seal Application Calculator
How to Use
In the boxes below, fill out the information that you have regarding the fog seal. Select which variable you need calculated and hit the calculate button.
(1) Application Rate (L/m2)
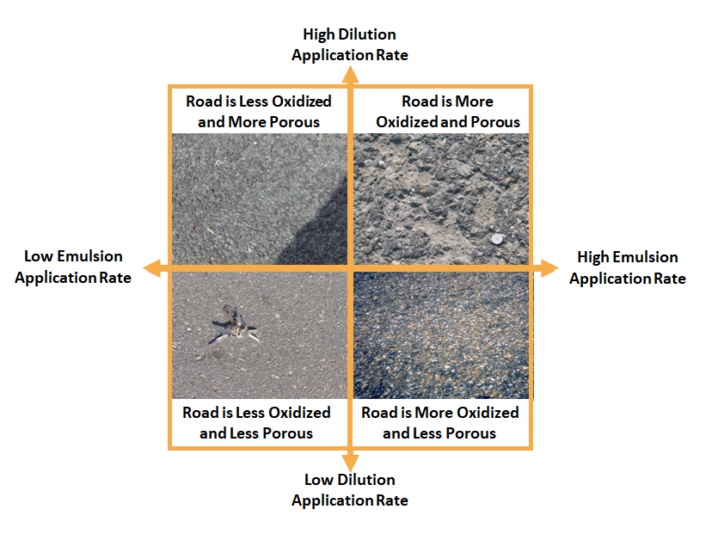
There are three types of application rate. The first two listed below are included in this calculator.
- Emulsion Application Rate: the rate of which emulsion purchased from a vendor is placed on the road
- Diluted Emulsion Application Rate: in some cases, fog seals must be diluted with water before they are applied. This variable described the application rate of the diluted mixture.
- Residual Application Rate: This describes how must material is left on the road after it has cured.
(1a) Emulsion Application Rate (L/m2)
(1b) Diluted Emulsion Application Rate (L/m2)
(2) Emulsion Type
(3) Road Dimensions (m)
(4) Distributor (L)
(5) Calculate
Further Information on Distributor Values